Configuring Proxy Sets
The Proxy Sets table lets you configure up to
| ● | The maximum number of addresses that you can configure in the Proxy Address table ("child" of the Proxy Sets table) per Proxy Set is |
| ● | The maximum number of supported DNS-resolved IP addresses per Proxy Set is |
| ● | The maximum number of supported DNS-resolved IP addresses for all Proxy Sets combined is |
| ● | An SRV query sent by the device can return up to 50 hostnames. For each hostname, the subsequent DNS A-record query sent by the device can resolve into up to 50 IP addresses. |
Multiple proxy servers enables you to implement proxy load balancing and redundancy. These features are supported by the device's proxy keep-alive feature, which when enabled, sends keep-alive messages (SIP OPTIONS) to all configured proxy servers to determine their connectivity status (offline or online). You can also configure the device to consider the proxy as offline if specific SIP response codes are received in response to the keep-alive messages. You can configure the number of required consecutive successful keep-alive messages before the device considers a previously offline proxy as online. This mechanism avoids the scenario in which the device falsely detects a proxy as being online when it is actually offline, resulting in call routing failure.
You can assign each Proxy Set a specific TLS Context (TLS configuration), enabling you to use different TLS settings (including certificates) per SIP entity (IP Group).
You can also enable the device to classify incoming SBC SIP dialogs to IP Groups, based on Proxy Set. If the source address of the incoming SIP dialog is the same as the address of a Proxy Set, the device classifies the SIP dialog as belonging to the IP Group that is associated with the Proxy Set.
To use a configured Proxy Set, you need to assign it to an IP Group in the IP Groups table (see Configuring IP Groups). When the device sends INVITE messages to an IP Group, it sends it to the address configured for the Proxy Set. You can assign the same Proxy Set to multiple IP Groups (belonging to the same SRD).
| ● | It is recommended to classify incoming SIP dialogs to IP Groups based on Classification rules (see Configuring Classification Rules) instead of based on Proxy Sets. |
| ● | For the Gateway application, you can view the device's connectivity status with proxy servers in the Tel-to-IP Routing table for Tel-to-IP routing rules whose destination is an IP Group that is associated with a Proxy Set. The status is only displayed for Proxy Sets enabled with the Proxy Keep-Alive feature. |
| ● | To view connectivity status of Proxy Sets, see Viewing Proxy Set Status. |
The Proxy Set is configured using two tables with parent-child relationship:
| ■ | Proxy Sets table (parent): Defines the attributes of the Proxy Set such as associated SIP Interface and redundancy features - ini file parameter [ProxySet] or CLI command, configure voip > proxy-set |
| ■ | Proxy Set Address table (child): Defines the addresses of the Proxy Set - table ini file parameter [ProxyIP] or CLI command, configure voip > proxy-ip > proxy-set-id |
| ➢ | To configure a Proxy Set: |
| 1. | Open the Proxy Sets table (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > Core Entities folder >Proxy Sets). |
| 2. | Click New; the following dialog box appears (screenshot has been cropped due to page size): |
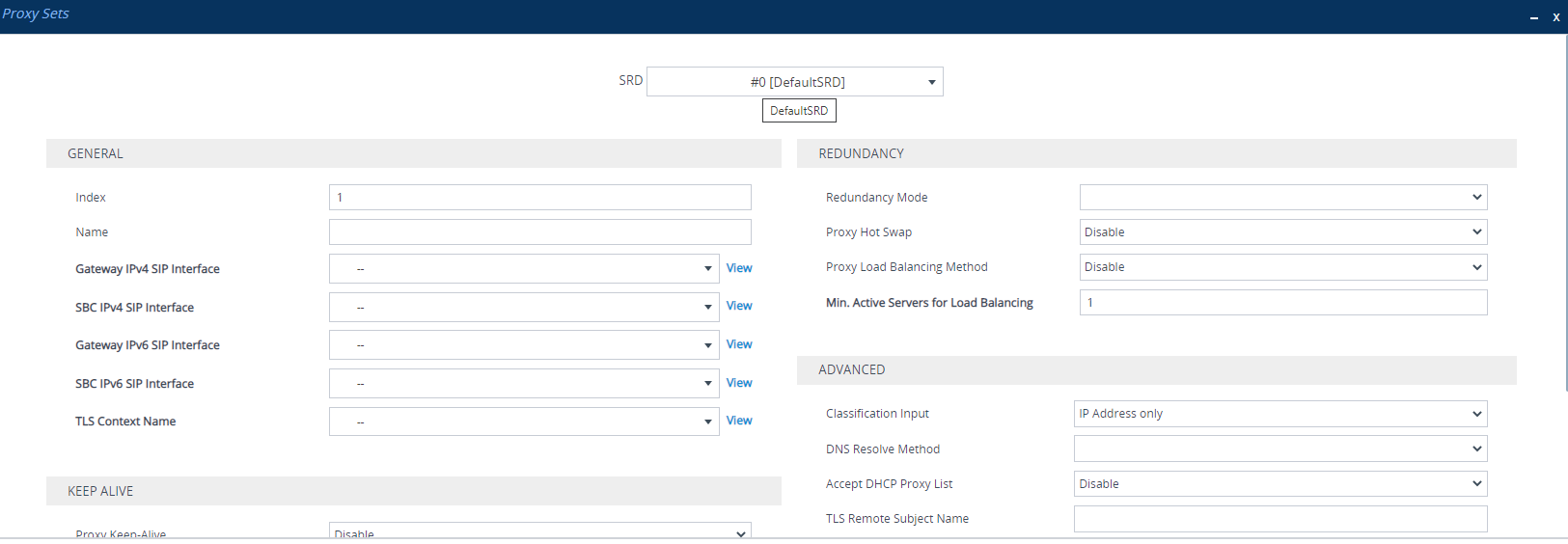
| 3. | From the 'SRD' drop-down list, select an SRD. |
| 4. | Configure a Proxy Set according to the parameters described in the table below. |
| 5. | Click Apply. |
| 6. | Configure proxy addresses for the Proxy Set: |
| a. | Select the index row of the Proxy Set that you added, and then click the Proxy Address link located below the table; the Proxy Address table opens. |
| b. | Click New; the following dialog box appears: |
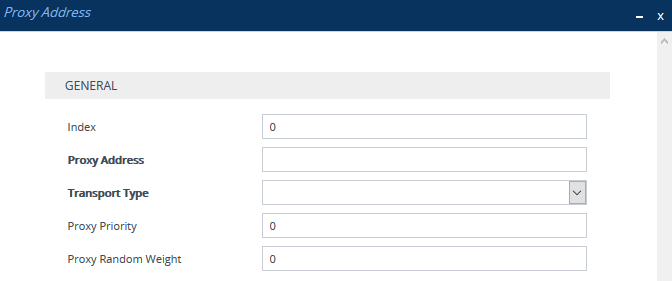
| c. | Configure the address of the Proxy Set according to the parameters described in the table below. |
| d. | Click Apply. |
Proxy Sets Table and Proxy Address Table Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
'SRD' voip-network proxy-set > srd-id [SRDName] |
Assigns an SRD to the Proxy Set. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
General |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Index' configure voip > voip-network proxy-set [Index] |
Defines an index number for the new table row. Note: Each row must be configured with a unique index. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Name' proxy-name [ProxyName] |
Defines a descriptive name, which is used when associating the row in other tables. The valid value is a string of up to 40 characters. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Gateway IPv4 SIP Interface' gwipv4-sip-int-name [GWIPv4SIPInterfaceName] |
Assigns an IPv4-based SIP Interface for Gateway calls to the Proxy Set. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'SBC IPv4 SIP Interface' sbcipv4-sip-int-name [SBCIPv4SIPInterfaceName] |
Assigns an IPv4-based SIP Interface for SBC calls to the Proxy Set. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Gateway IPv6 SIP Interface' gwipv6-sip-int-name [GWIPv6SIPInterfaceName] |
Assigns an IPv6-based SIP Interface for Gateway calls to the Proxy Set. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'SBC IPv6 SIP Interface' sbcipv6-sip-int-name [SBCIPv6SIPInterfaceName] |
Assigns an IPv6-based SIP Interface for SBC calls to the Proxy Set. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'TLS Context Name' tls-context-name [TLSContextName] |
Assigns a TLS Context (TLS configuration) to the Proxy Set. By default, no TLS Context is assigned. If you assign a TLS Context, the TLS Context is used as follows:
To configure TLS Contexts, see Configuring TLS Certificates. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Keep Alive |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Keep-Alive' proxy-enable-keep-alive [EnableProxyKeepAlive] |
Enables the device's Proxy Keep-Alive feature, which checks connectivity with all the proxy servers of the Proxy Set, by sending keep-alive messages.
Note:
Instead of sending the initial keep-alive messages simultaneously, you can configure the device, using the global [ProxyKeepAliveRandomization] parameter, to randomize the time at which each Proxy Set starts its keep-alive process. When you configure a randomized time range (between 1 and N seconds), the device begins the keep-alive mechanism of each Proxy Set at a different randomized time within this window range. Only the first keep-alive message per Proxy Set is randomized; subsequent keep-alive messages of each Proxy Set follow the normal interval configured by the 'Proxy Keep-Alive Time' parameter (see below). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Keep-Alive Time' proxy-keep-alive-time [ProxyKeepAliveTime] |
Defines the interval (in seconds) between keep-alive messages sent by the device when the Proxy Keep-Alive feature is enabled (see the 'Proxy Keep-Alive' parameter in this table). The valid range is 5 to 2,000,000. The default is 60. Note: The parameter is applicable only if you configure the 'Proxy Keep-Alive' parameter to Using OPTIONS, Using OPTIONS on Active Server or Using Fake REGISTER. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Keep-Alive Failure Responses' keepalive-fail-resp [KeepAliveFailureResp] |
Defines SIP response codes that if any is received in response to a keep-alive message using SIP OPTIONS (Using OPTIONS or Using OPTIONS on Active Server) or using fake REGISTER requests (Using Fake REGISTER), the device considers the proxy as offline. Up to three response codes can be configured, where each code is separated by a comma (e.g., 407,404). By default, no response code is defined. If no response code is configured, or if response codes received are not those configured, the proxy is considered online. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Success Detection Retries' success-detect-retries [SuccessDetectionRetries] |
Defines the minimum number of consecutive, successful keep-alive messages that the device sends to an offline proxy, before the device considers the proxy as online. The interval between the sending of each consecutive successful keep-alive is configured by the 'Success Detection Interval' parameter (see below). For an example of using this parameter, see the 'Success Detection Interval' parameter. The valid range is 1 to 100. The default is 1. Note: The parameter is applicable only if you configure the 'Proxy Keep-Alive' parameter to Using OPTIONS, Using OPTIONS on Active Server or Using Fake REGISTER. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Success Detection Interval' success-detect-int [SuccessDetectionInterval] |
Defines the interval (in seconds) between each successful keep-alive retries (as configured by the 'Success Detection Retries' parameter) that the device performs for offline proxies. The valid range is 1 to 200. The default is 10. For example, assume that the ‘Success Detection Retries’ parameter is configured to 3 and the ‘Success Detection Interval’ parameter to 5 (seconds). When connectivity is lost with the proxy, the device sends keep-alive messages to the proxy. If the device receives a successful response from the proxy, it sends another (1st) keep-alive after 5 seconds, and if successful, sends another (2nd) keep-alive after 5 seconds, and if successful, sends another (3rd) keep-alive after 5 seconds, and if successful, considers connectivity with the proxy as being restored. Note: The parameter is applicable only if you configure the 'Proxy Keep-Alive' parameter to Using OPTIONS, Using OPTIONS on Active Server or Using Fake REGISTER. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Failure Detection Retransmissions' fail-detect-rtx [FailureDetectionRetransmissions] |
Defines the maximum number of UDP retransmissions that the device sends to an offline proxy before the device considers the proxy as offline. The valid range is -1 to 255. The default is -1, which means that the setting of the global parameter [SIPMaxRtx] is applied. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Redundancy |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Redundancy Mode' proxy-redundancy-mode [ProxyRedundancyMode] |
Enables proxy redundancy.
Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Hot Swap Mode' is-proxy-hot-swap [IsProxyHotSwap] |
Enables the Proxy Hot-Swap feature. When this feature is enabled and the device sends a SIP-dialog initiating request (e.g., INVITE or REGISTER) to the proxy server and the message fails, the device automatically tries to send the same message to a redundant proxy server (IP address) configured for the Proxy Set. If that attempt also fails, the device continues to retry with the next proxy in the list, and so on (up to a maximum of The redundant proxy is determined by your Proxy Set configuration ('Redundancy Mode' and 'Proxy Load Balancing Method' parameters).
However, if you've configured an SBC Alternative Routing Reasons Set for the IP Group (see Configuring SIP Response Codes for Alternative Routing Reasons), the device tries up to four online proxies in the Proxy Set. If it successfully connects to one of the redundant proxies, it re-sends the message to this proxy. This functionality doesn’t apply to REGISTER requests initiated by the device (e.g., for Accounts).
Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Load Balancing Method' proxy-load-balancing-method [ProxyLoadBalancingMethod] |
Enables load balancing between proxy servers in the Proxy Set.
For DNS-resolved IP addresses for proxy servers configured with an FQDN (including NAPTR and SRV, if configured), the priority is received from the DNS. The IP address list is refreshed every user-defined interval, configured by the [ProxyIPListRefreshTime] parameter. If a change in the order of the IP address entries in the list occurs, all load statistics are erased and balancing starts over again. For the Gateway application, REGISTER messages are also distributed in a round-robin fashion, unless you have configured a specific IP address of a registrar server (using the [RegistrarIP] parameter).
For proxy servers configured with an FQDN, the weight of each DNS-resolved IP address is received from the DNS server (using SRV records). However, if you have configured the weight for the FQDN in the 'Proxy Random Weight' parameter, this parameter's value overrides the weight from the DNS server. The device sends the requests in such a fashion that each proxy receives a percentage of the requests according to its' weight. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Min. Active Servers for Load Balancing' min-active-serv-lb [MinActiveServersLB] |
Defines the minimum number of proxies in the Proxy Set that must be online for the device to consider the Proxy Set as online, when proxy load balancing is used. The valid value is 1 to 15. The default is 1. Note: The parameter is applicable only if proxy load balancing is enabled (see the 'Proxy Load Balancing Method' parameter, above). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Advanced |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Classification Input' classification-input [ClassificationInput] |
Defines how the device classifies incoming IP calls to the Proxy Set.
Note:
If multiple Proxy Sets are configured with the same IP address but associated with different SIP Interfaces, then classification based on Proxy Set can be correctly achieved. If multiple Proxy Sets are configured with the same IP address and SIP Interface, but with different ports (e.g., 10.1.1.1:5060 and 10.1.1.1:5070) and the parameter is configured to IP Address, Port & Transport Type, classification to the correct IP Group is achieved. Therefore, when classification is by Proxy Set, pay attention to the configured IP addresses and this parameter. When multiple Proxy Sets are configured with the same IP address, the device selects the matching Proxy Set in the following order:
For example:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'DNS Resolve Method' dns-resolve-method [DNSResolveMethod] |
Defines the DNS query record type for resolving the proxy server's hostname / domain name (FQDN) into an IP address(es).
The SRV query returns the host names (and their weights). The device then performs DNS A-record queries per host name (according to the received weights) to resolve into IP addresses. Note: The device caches the DNS-resolved IP addresses of the last successful DNS query of a Proxy Set. The device uses the cache if the DNS server goes offline. This functionality occurs regardless of the setting of the [DNSCache] parameter. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Accept DHCP Proxy List' accept-dhcp-proxy-list [AcceptDHCPProxyList] |
Enables the device to obtain the Proxy Set's address(es) from a DHCP server. When enabled, it sends a DHCP request with Option 120 (SIP server address) to a DHCP server. This occurs upon a DHCP refresh (lease renewal). When the device receives the list of IP addresses (or DNS) from the server, it adds them to the Proxy Set (replaces any existing IP addresses or DNS).
Note: When enabled, the device uses UDP and port 5060. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'TLS Remote Subject Name' tls-remote-subject-name [TLSRemoteSubjectName] |
Defines the Subject Name of the TLS certificate received from the remote side when establishing a TLS connection with the Proxy Set. When the device receives a certificate from the remote side, it validates the certificate by comparing the certificate's Subject Alternative Names (SAN) with the Proxy Set's addresses (IP address and FQDN) and the parameter's value. If a SAN matches an address or the parameter's value, the device considers the certificate as valid and establishes the TLS connection and allows the call. If there is no match and the SAN is marked as "critical", the device doesn’t establish a TLS connection and rejects the call. If there is no match and the SAN isn't marked as "critical", the device compares the Proxy Set's addresses (IP address and FQDN) and the parameter's value with the certificate's Common Name (CN). If any of them match, the device establishes a TLS connection and allows the call; otherwise, it doesn't establish a TLS connection and rejects the call. The valid value is a string of up to 100 characters. By default, no value is defined. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Peer Host Name Verification Mode' peer-host-name-verification-mode [PeerHostNameVerificationMode] |
Enables the device to verify the Subject Name of the TLS certificate received from the remote side for authentication and establishing a TLS connection.
If the device receives a certificate from a SIP entity (IP Group) and the parameter is configured to Server Only or Server & Client (or global parameter is used and configured to one of these options), it attempts to authenticate the certificate based on the certificate's address:
Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'TCP/TLS Connection Reuse' connection-reuse [ConnectionReuse] |
Enables the reuse of the initially established TCP or TLS connection between the device and the proxy server for all subsequent SIP requests sent to the proxy server. New out-of-dialog requests (e.g., INVITE or REGISTER) use the same secured connection. One of the benefits of enabling the parameter is that it may improve performance by eliminating the need for additional TCP/TLS handshakes with the proxy, allowing sessions to be established rapidly.
Note: For SIP responses, the device always uses the TCP/TLS connection of the corresponding incoming SIP request, regardless of the parameter's setting. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'In-Call Route Mode' in-call-route-mode [InCallRouteMode] |
Enables the device to send in-call SIP messages (e.g., re-INVITE and BYE) to the currently active proxy if the proxy to which the dialog-initiating INVITE message was sent is currently offline. This is applicable when the Proxy Set has multiple proxies (IP addresses). This feature occurs even if the currently active proxy was offline when the call was established.
Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Proxy Address Table |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Index' proxy-ip-index [ProxyIp_ProxyIpIndex] |
Defines an index number for the new table row. Note: Each row must be configured with a unique index. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Address' proxy-address [ProxyIp_IpAddress] |
Defines the address of the proxy server (Proxy Set). The address can be defined as an IP address in dotted-decimal notation (e.g., 201.10.8.1) or FQDN. You can also specify the port using the following format:
Note:
However, configuring multiple Proxy Sets with the same IP address, but with different SIP Interfaces is acceptable for classifying incoming SIP requests to source IP Groups based on Proxy Set. For more information on determining the Proxy Set, see the 'Classification Input' parameter (above) parameter . |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Transport Type' transport-type [ProxyIp_TransportType] |
Defines the transport type for communicating with the proxy.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Priority' priority [ProxyIp_Priority] |
Defines the priority of the proxy. When a proxy server goes offline, the device attempts to connect to an online proxy server that has the highest priority. The valid value is 0 to 65535, where 0 is the highest priority and 65535 the lowest. The default is 0. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
'Proxy Random Weight' weight [ProxyIp_Weight] |
Defines the weight of the proxy. The valid value is 0 to 65535, where 0 is the highest weight and 65535 the lowest. The default is 0. Note:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||